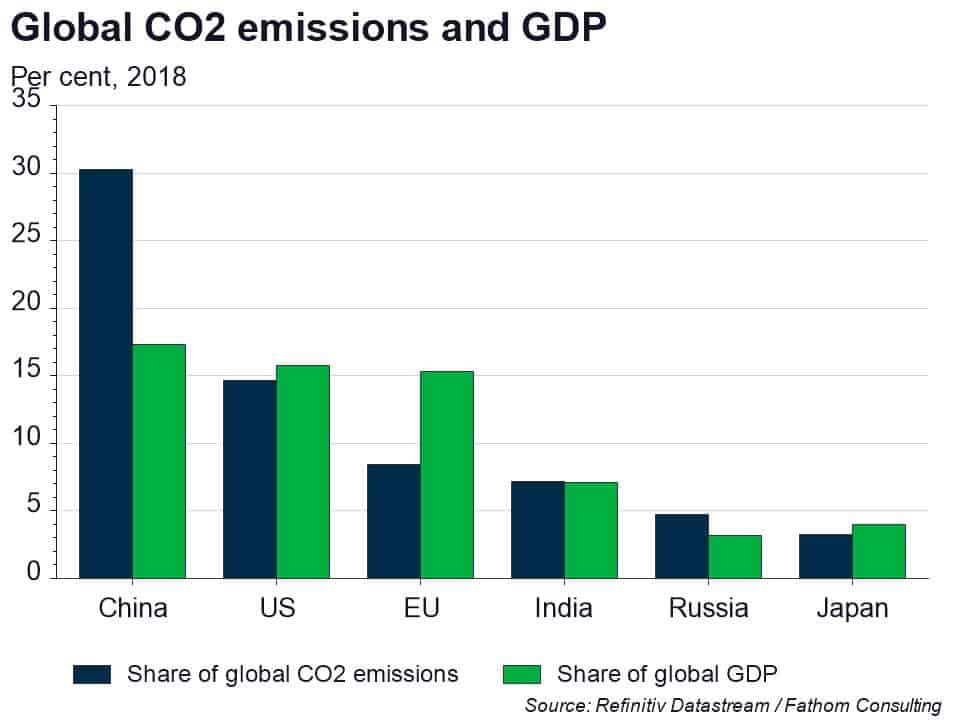
China is the world’s largest emitter, accounting for 30 per cent of the world’s CO2 emissions in 2020. China’s current target is for emissions to peak before 2030 and to achieve carbon neutrality by 2060. Both goals are widely considered inadequate and inconsistent with the Paris goals of limiting global warming to below 2.0°C, and preferably to 1.5°C, compared to pre-industrial levels. To get even close to the Paris goals, net zero needs to be achieved by 2050 and emissions need to start falling now, not in nine years’ time. China will need to change its energy mix and reduce its reliance on coal…
[Please click below to read the full note.]